Dermatology is inherently a visual discipline, relying heavily on clinical and histopathologic experience and interpretation. However, many skin conditions share overlapping clinical and histopathological features. As a result, even experienced clinicians and dermatopathologists may face diagnostic uncertainty. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial, as it directly impacts therapeutic decisions and ultimately determines treatment success, thereby reducing the burden on patients.
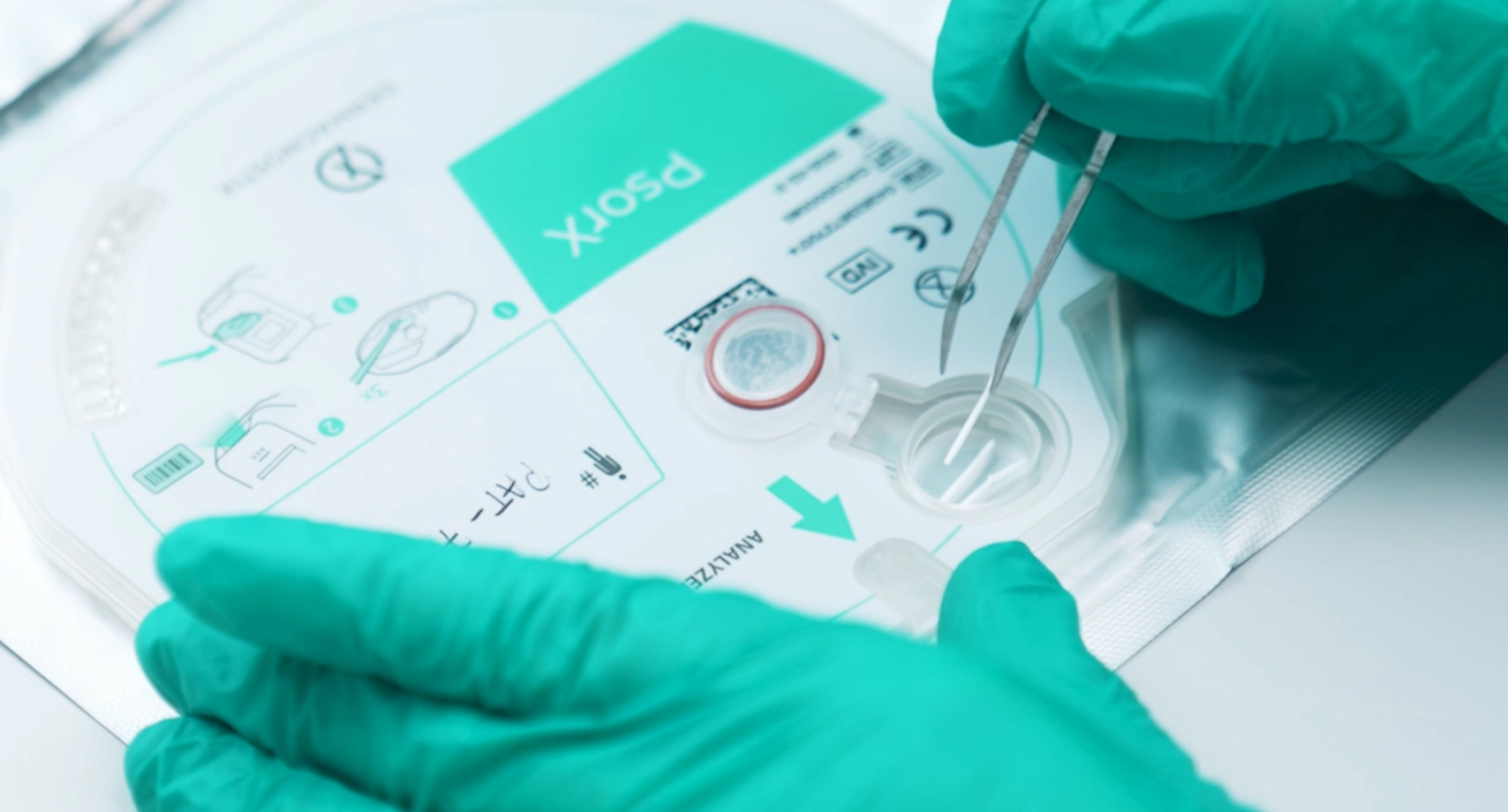
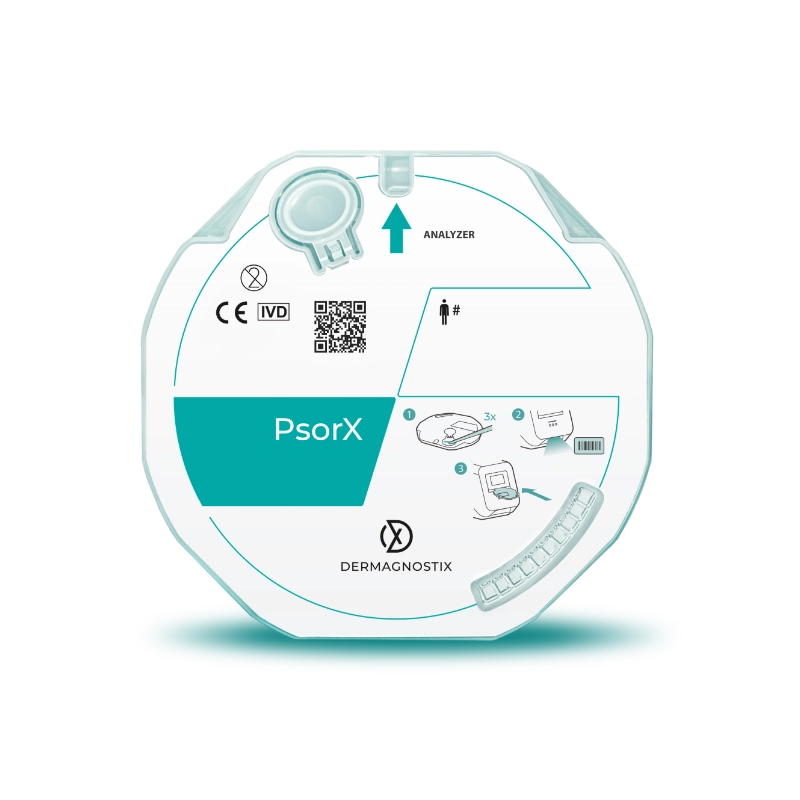
The LabDisk product line provides a standardized, automated molecular workflow to support dermatopathologists in clarifying complex cases. By analyzing gene expression patterns from FFPE samples, LabDisk enables objective molecular insights that complement histology, offering clarity when conventional methods reach their limits. Within this portfolio, PsorX provides molecular support for differentiating psoriasis and eczema, while LymphX (coming soon) will extend this approach to distinguishing early Mycosis Fungoides from benign inflammatory skin conditions.
As a fully integrated cartridge-based system, each LabDisk runs on the Dermagnostix Analyzer, delivering reproducible molecular results using a streamlined, lab-ready process. No additional specialized molecular equipment is required.
Elevate your dermatopathology practice with molecular diagnostics – contact us today to learn more!