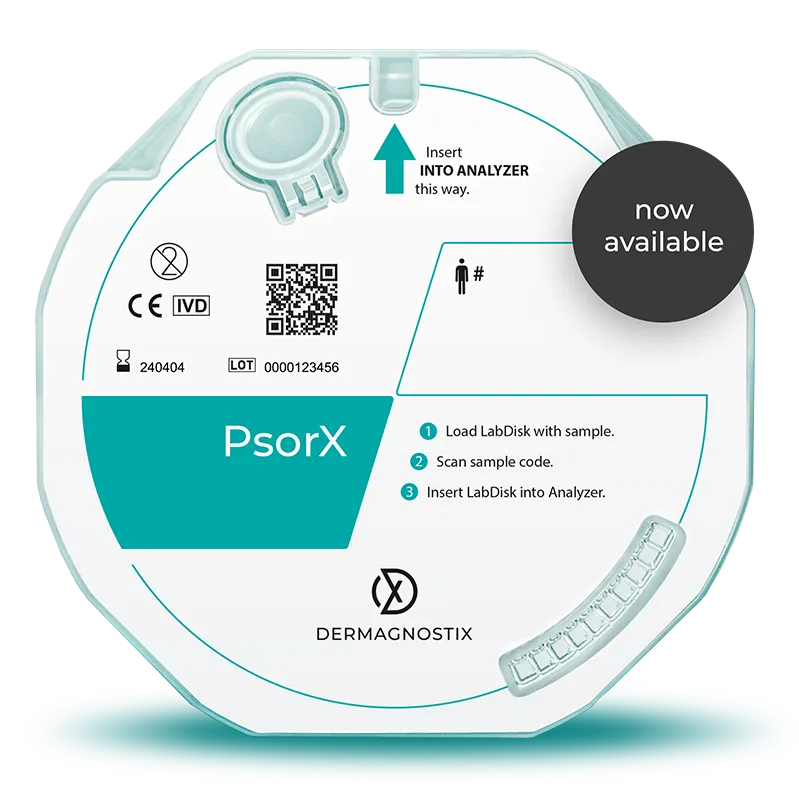
PsorX (CE-IVD) – a breakthrough for inflammatory skin diseases
PsorX detects the molecular signature of psoriasis versus eczema supporting the reliable differential diagnosis of these diseases.
Based on the gene expression of NOS2 and CCL27, PsorX accurately and efficiently distinguishes these diseases, even in cases where conventional diagnostic methods failed¹’
Psoriasis
“Significant knowledge regarding psoriasis and advancement in psoriasis treatment have been gained over the past 30 years. Despite this, in review of the currently available highest level of evidence, the expert work group acknowledges that much has yet to be learned…There is also an important need to identify biomarkers that can potentially predict the appropriate biologic agent for individual patients.” ³
Background

Pipeline products
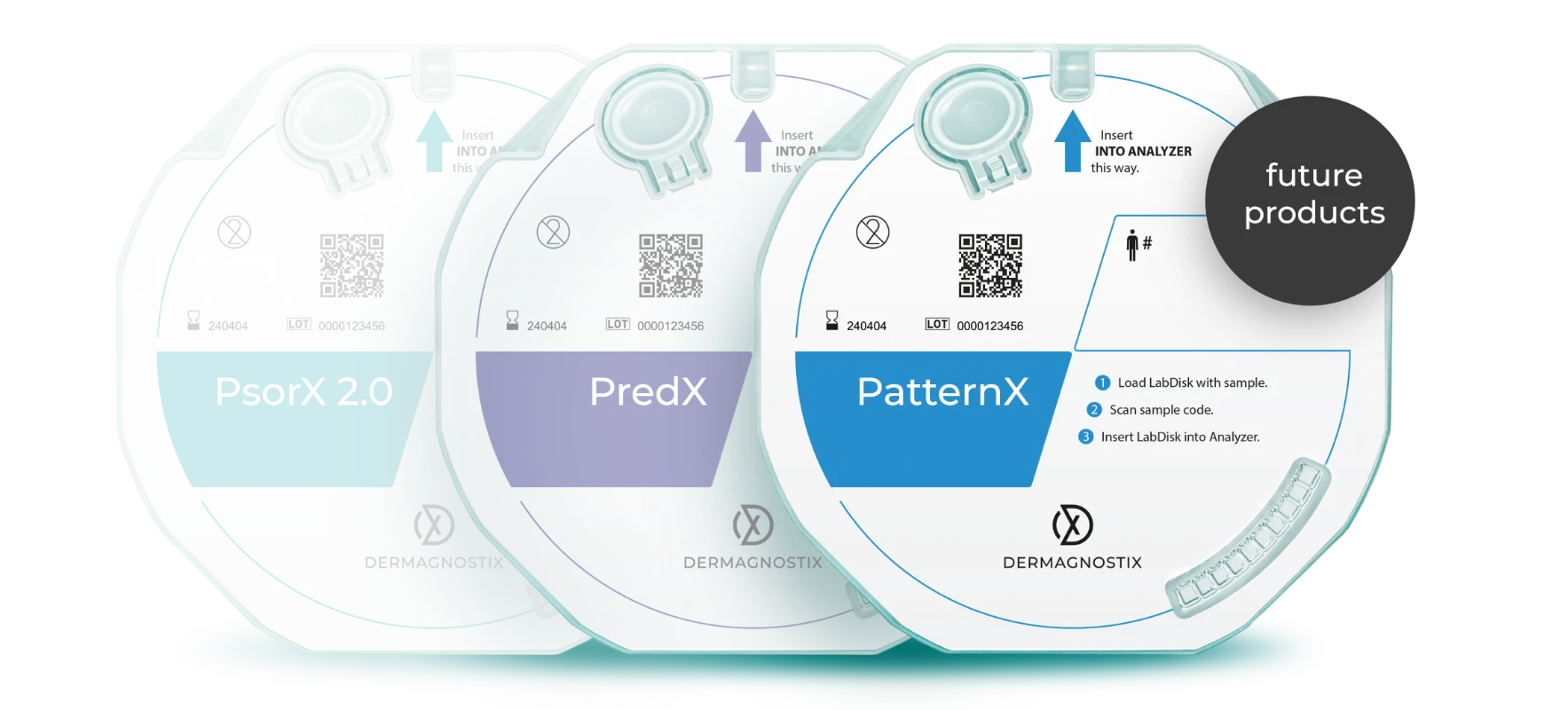
PatternX
Background
PredX
Background
“For atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, a broad spectrum of innovative treatments has been developed. However, treatment responses cannot be predicted so far. Hence, development of (bio)markers allowing selection of specific medications for individual patients is needed.” ⁶
Mycosis fungoides
(PsorX 2.0)
Background
“The diagnosis of early MF (patch stage) is particularly challenging […] This diagnosis might be elusive because MF in its early stage shares clinical and histopathological features with inflammatory benign dermatoses…and immunohistochemistry and molecular analysis have limited utility as isolated criteria" ⁷
References
- Garzorz-Stark N, Krause L, Lauffer F, Atenhan A, Thomas J, Stark SP, Franz R, Weidinger S, Balato A, Mueller NS, Theis FJ, Ring J, Schmidt-Weber CB, Biedermann T, Eyerich S, Eyerich K (2016): A novel molecular disease classifier for psoriasis and eczema. Experimental Dermatology 25(10): 767-774.
- Quaranta M, Knapp B, Garzorz-Stark N, Mattii M, Pullabhatla V, Pennino D, Andres C, Traidl-Hoffmann C, Cavani A, Theis F, Ring J, Schmidt-Weber C, Eyerich S, Eyerich K (2014): Intraindividual genome expression analysis reveals a specific molecular signature of psoriasis and eczema. Science translational medicine 6(244): 244ra90-244ra90.
- Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, Kivelevitch D, Prater EF, Stoff B, Armstrong AW, Connor C, Cordoro KM, Davis DMR, Elewski BE, Gelfand JM, Gordon KB, Gottlieb AB, Kavanaugh A, Kiselica M, Korman NJ, Kroshinsky D, Lebwohl M, Leonardi CL, Elmets CA (2019): Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 80(4): 1029-1072.
- Kolesnik M, Franke I, Lux A, Quist S, Gollnick HP (2018): Eczema in psoriatico: An important differential diagnosis between chronic allergic contact dermatitis and psoriasis in palmoplantar localization. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 98(1): 50-58.
- Gromova M, Vaggelas A, Dallmann G, Seimetz D (2020): Biomarkers: opportunities and challenges for drug development in the current regulatory landscape. Biomarker Insights 15: 1177271920974652.
- Ujiie H, Rosmarin D, Schön MP, Ständer S, Boch K, Metz M, Thaci D, Schmidt E, Cole C, Amber KT, Didona D, Hertl M, Recke A, Grasshoff H, Hackel A, Schumann A, Riemekasten G, Bieber K, Sprow G, Dan J, Zillikens D, Sezin T, Christiano AM, Wolk K, Sabat R, Kridin K, Werth VP, Ludwig RJ (2022): Unmet medical needs in chronic, non-communicable inflammatory skin diseases. Frontiers in medicine 9:875492.
- Torres-Cabala CA (2020): Diagnosis of T-cell lymphoid proliferations of the skin: putting all the pieces together. Modern Pathology 33:83-95.